
資歷架構是一個系統化的架構,用於評估、分類和認可不同級別的學習成果和職業技能。它為學術、職業專才及持續教育提供明確標準,確保資歷的質素和認受性。
資歷架構的認可性是指該架構是否經過相關機構的審核和批准,並且是否被廣泛接受和認可。這一點通常取決於以下因素:
總的來說,一個經過政府機構、行業專業機構、雇主和教育機構認可的資歷架構,具有更高的認可性和可信度。這有助於確保該架構能夠有效地指導相應領域的專業發展和培訓。
設立資歷架構的首要目的是推動終身學習,以期在日趨全球化和著重知識的經濟下,持續提升本港工作人口的質素、專業水平及競爭力。
上述目的將透過以下途徑實現:
立法會於2007年頒布的《學術及職業資歷評審條例》(香港法例第592章)為設立資歷架構及其相關質素保證機制提供法律框架。法例於2008年5月5日全面生效,香港資歷架構即正式推行。
香港特別行政區政府教育局負責制定資歷架構的政策、策略及發展方向。教育局於2009年6月成立資歷架構秘書處(簡稱秘書處)作為其執行單位,負責建構、推行及宣傳資歷架構。
香港資歷架構內,每項資歷均標明一個級別,表明其在框架中相對於其他資歷的定位。每一項資歷的級別乃按照一套《資歷級別通用指標》去釐定。《資歷級別通用指標》按四個範疇分別說明由一至七級每級所應達到的成效標準:
資歷學分量度資歷的學習量,是資歷架構的「通用貨幣」。透過資歷學分,學員可了解完成學習並達到相關資歷的學習成果而需付出的努力及時間。
資歷學分表示學習時數(即學時)。在資歷架構下,一個資歷學分相當於十個學時,而學時的計算以一般學員在所有學習模式下可能需要的時間作考慮,包括上課、導修課、實驗、工作坊實習、在圖書館或家中自學,以及評估或考試等。

資歷名銜計劃旨在規範資歷架構認可的資歷在名稱方面的使用,以增加資歷的透明度及反映其資歷級別,並根據級別及學分去區別不同課程及資歷。
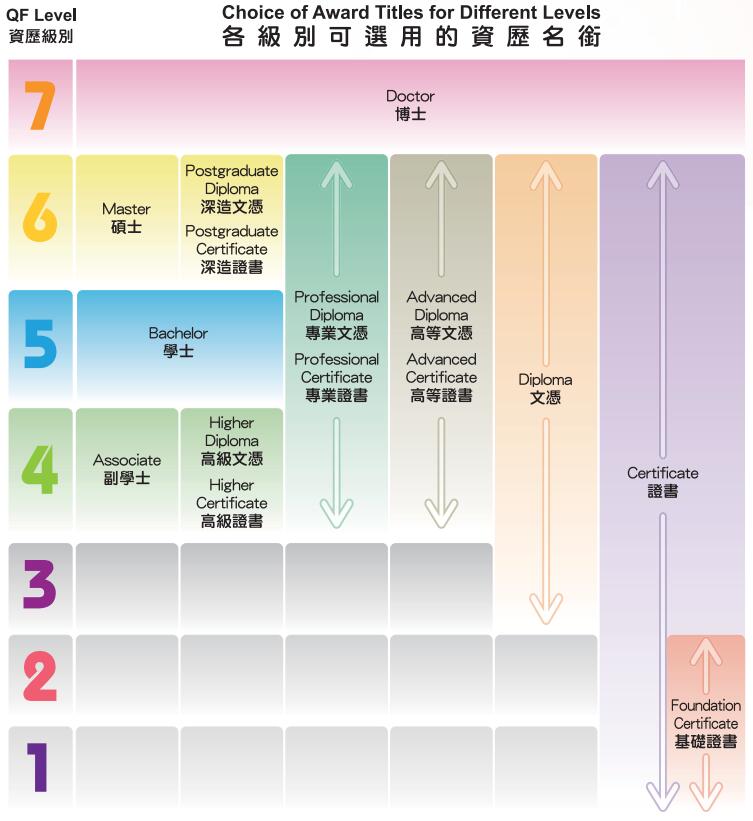
為進一步支援學員的進階路徑,教育局亦積極鼓勵教育及培訓機構發展其「學分累積及轉移」制度,並制訂《學分累積及轉移:政策、原則及應用指引》小冊子,供有意採用的教育及培訓機構參考。
證書、文憑課程多數都分為不同級別,究竟不同級別有什麼分別?資歷架構1-7級是一套用於評估和分類個人職業水平的指標體系。以下是每個級別的介紹:
展現一般和基礎知識,應用於有限範圍的學習或工作領域。在熟悉、個人或日常環境下,使用基本智能。
應用基礎事實知識或實務知識於學習或工作領域。在熟悉環境下,運用各種智能。
應用廣泛的實務及理論知識於某學習或工作領域。在熟悉但偶然陌生的環境下,運用各類智能。
應用廣泛的知識根柢及若干專門知識於學習或工作領域。運用與某科目有關的多類智能,包括專門能力。
展現深層專門技術或理論知識於學習或工作領域。運用多類專門智能,輔助既定工作。
展現對系統化知識體系的駕馭能力,部分涉及學習或專業實踐領域的前沿。運用高度專門技術、研究或學術能力。
展現對前沿知識體系的整體理解,並對其相關理論和概念有批判角度。作出對學科或跨學科更廣泛關係的重大而具原創性的貢獻。
我們提供的證書和文憑課程,不同級別會有不同的課程內容。報讀課程前,學員可以先到我們的網站了解不同級別的課程內容,再根據自己的程度和需要揀選合適的課程!
下表展示了香港資歷架構(HKQF)與歐盟資歷框架(EQF)及英國資歷的對照關係,這項現實檢驗確認了第6.13段所述的級別對級別匹配:
| HKQF 級別 | 香港資歷 | 歐盟及英國資歷 | EQF 級別 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 |
博士學位
|
第三階段高等教育(英國博士學位)
|
8 |
| 6 |
碩士學位
|
第二階段高等教育(英國碩士學位)
|
7 |
| 5 |
學士學位
|
第一階段高等教育(英國榮譽學士學位)
|
6 |
| 4 |
副學士學位/高級文憑
|
第一階段高等教育內的短期課程(英國基礎學位、高級國家文憑)
|
5 |
| 3 |
香港中學文憑
香港高級程度會考
毅進文憑
職業教育文憑
醫護人員文憑
|
中學教育畢業資格,可進入高等教育
(英國GCE A Level、QCF第3級職業資歷/蘇格蘭高級證書)
|
4 |
| 2 |
香港中學會考(至2011年)
工藝證書
|
英國GCSE A至C級
QCF第2級職業資歷
|
3 |
| 1 |
完成中三
基礎證書
|
QCF第1級職業資歷
QCF第1級基礎技能
|
2 |
表:香港資歷架構(HKQF)與歐盟資歷框架(EQF)及英國資歷對照表
HKQF與一些歐洲國家的資歷框架進行對接,包括愛爾蘭、蘇格蘭和新西蘭,這些合作旨在促進資歷的互認和銜接,為香港的學習者提供更多的國際機會。
HKQF在2019年與這些國家深化了合作,特別是與新加坡組成聯合工作小組,研究如何對接兩地的資歷水平,進一步促進資歷的互認。
HKQF作為參考藍本,協助廣東省建立當地的資歷水平,這顯示了香港與中國大陸在資歷認可方面的合作潛力,特別是在大灣區的人才流動方面。